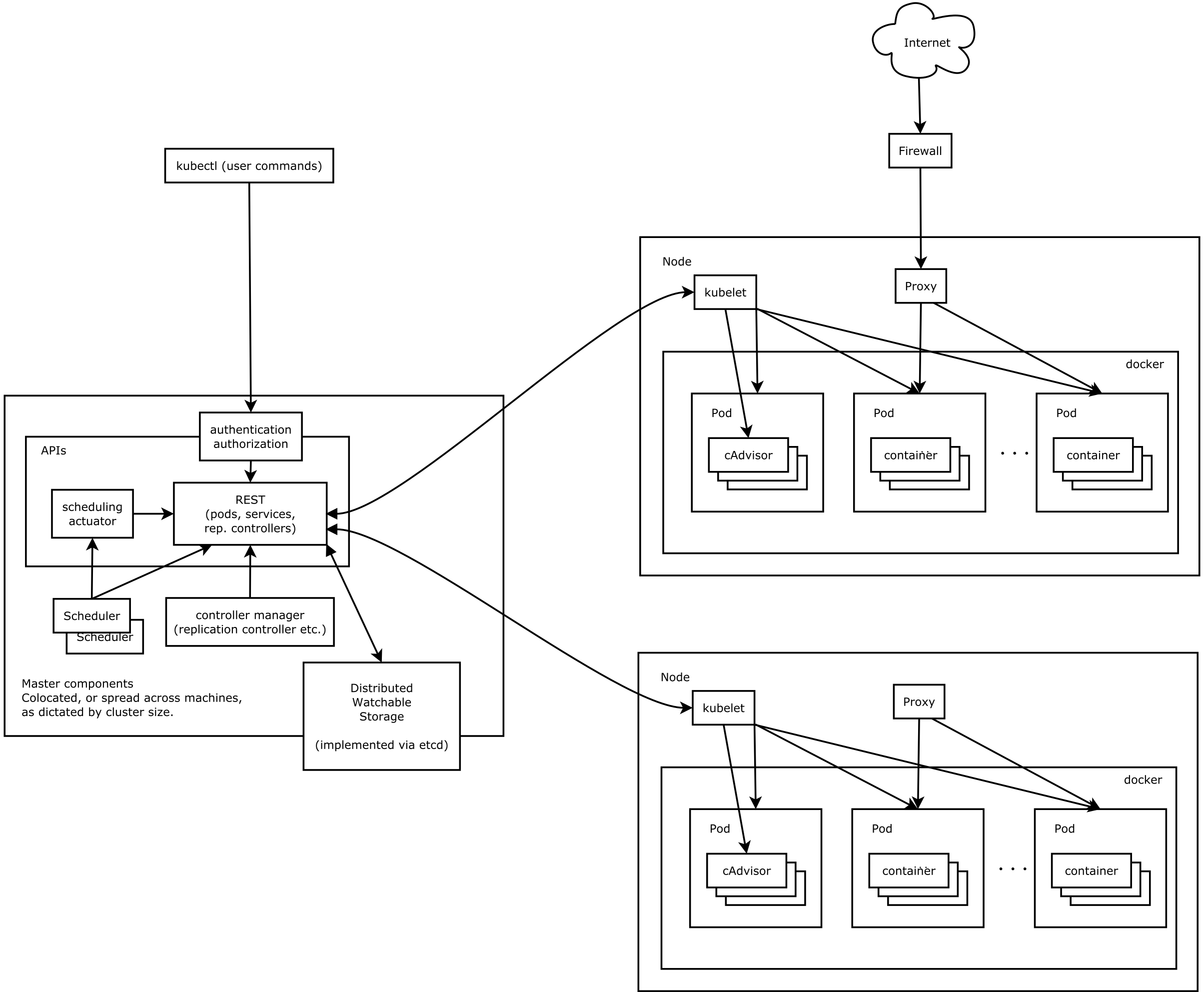
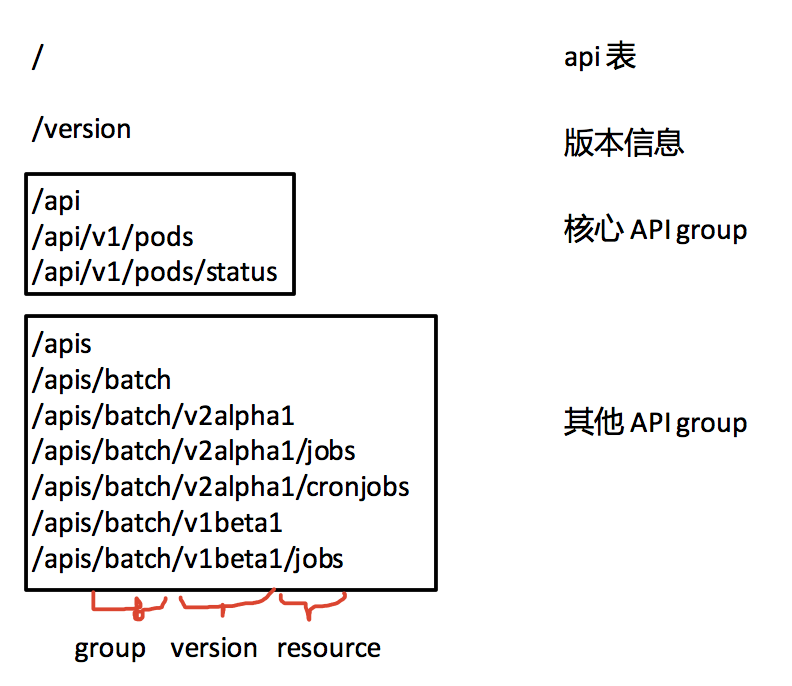
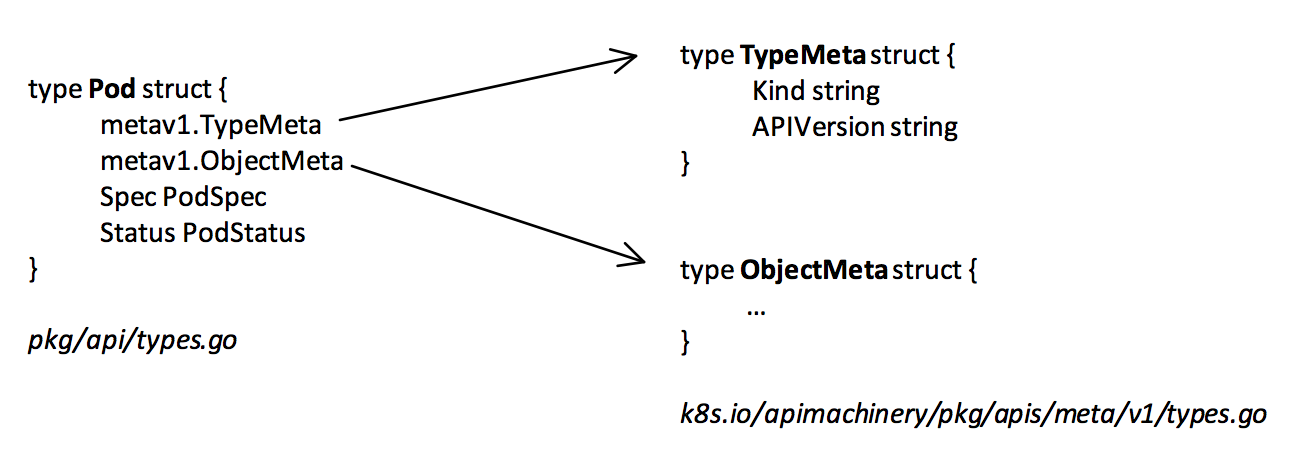
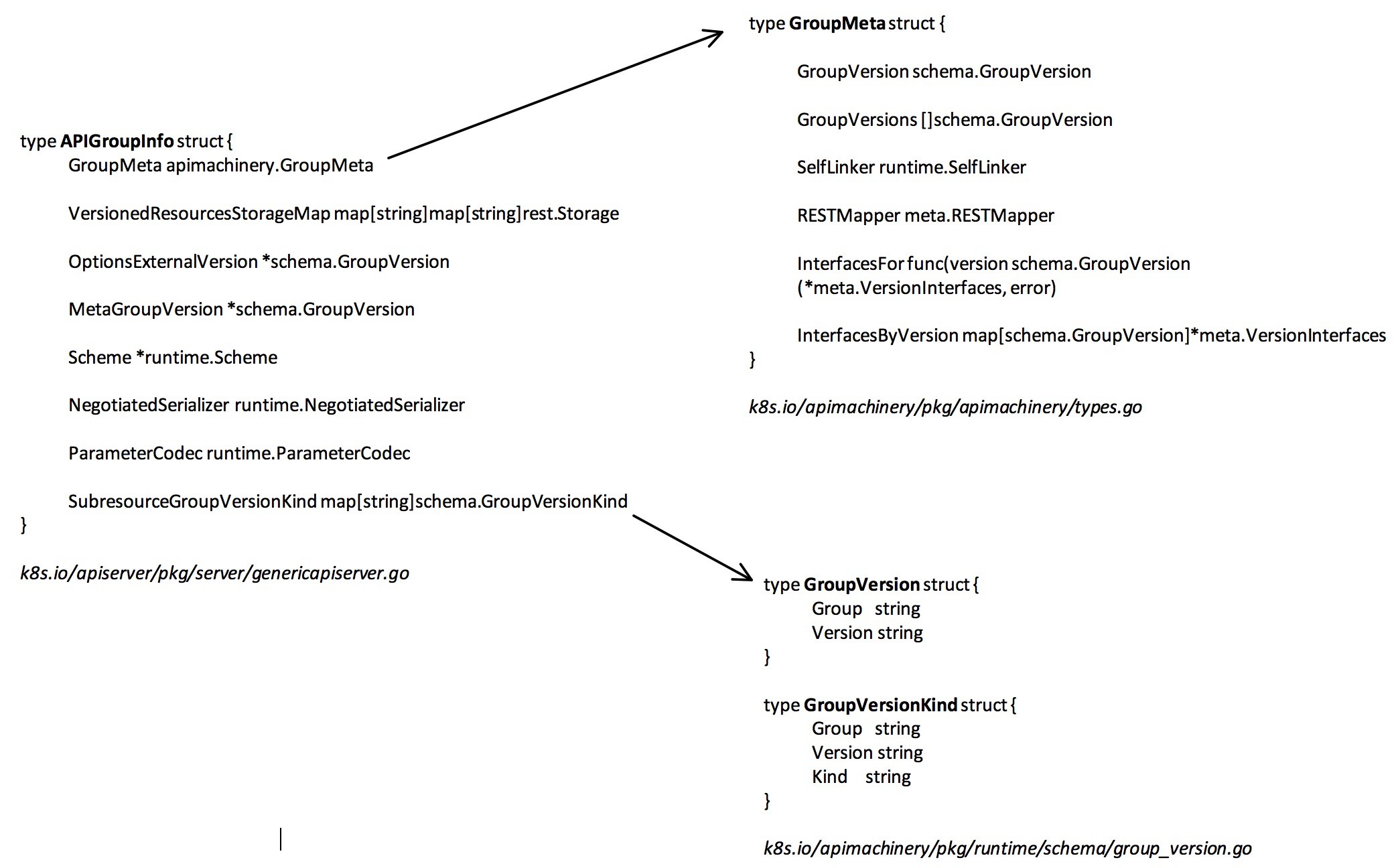
Paxos 总结
Paxos 是什么
Paxos is a mechanism for achieving consensus on a single value over unreliable communication channels.
Paxos 就是一个在不稳定的网络环境下建立的对一个值的共识。我们说的 Multi-Paxos 是指对多个值的共识,不过我们先一步一步来。
在 Paxos 中是没有 leader 这个概念的,所以相对来说会比较慢,因为谁都可以处理请求并且把自己的 peer 盖掉导致冲突,达成一致的过程会更长。
Paxos 只抵抗机器崩溃,网络异常,不抵抗恶意行为的节点,或者说使用不同协议的参与者,或者说参与者不能撒谎,所以经典的 Paxos 不抵抗拜占庭问题(也有针对拜占庭问题的 Paxos 带了 verify 的过程)。
Paxos 论文里面描述的算法,其实不是很清晰,一般人看了都会有疑问,所以后来很多人对这个算法做了补充和解释,包括作者本人。
基本需求
第一个是安全性,就是只有一个值会被选择,并且节点对这个值不会主动知道,而是在值被选择以后被动学习知道这个值被选择的(这个原文有点难懂我换成了自己的话解释了一下)。
第二个是活性,也就是值最终会被选择,并且所有节点会最终学习到这个值被选择了。
解决方案
首先单点可以排除,因为单点虽然是最容易解决一致性问题的,但是如果单点挂了,整个就不可用了,所以显然不能依靠单点。
![[single point]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/quorum-base.png)
那如果每个节点就接受自己接受到的第一个值,也会有平票问题(split votes)。red 和 blue 对等的,那到底谁被选择了呢,所以来了就接受的策略并不可行。
![[split votes]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/split-votes.png)
Paxos 是 quorum based 的,表示的一致性协议是少数服从多数的,在大多数节点都接受了这个值以后,这个值就被选择了。为了让节点可以接受多个值,多个值之间需要区分,所以就有了提交号,这个号码是单增的,拒绝掉小号的提交,并且当一个值已经被选择,那么之后的提交都要提交这个值,这样做的目的是让提交者知道这个值被学习了,是大家认可的一个值。有了少数服从多数原则,就会碰到冲突的问题。
这种情况就是下面这样,从时间上来讲,red 已经被选择了,如果 S3 能够拒绝 red 的提交,那么 S3,S4,S5就可以拿着 red 重试,并且知道 red 已经被大多数人接受了,而知道冲突的 S3 就会决绝这次请求,这个点上就处理了两个值(接受了一个拒绝了一个)。
![[conflict 1]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/conflict.png)
序列号可以帮助我们区分优先关系,这样因为网络问题延迟的请求就可以被处理。下面这种情况,red 虽然先提交,但是并不是先被大多数接受的(存在网络延迟),这个时候blue已经被选择了(被大多数人接受),我们需要提交 red 的提交意识到自己已经太“老”了,而触发这就是接受了 blue 的 S3。
![[conflict 2]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/conflict-1.png)
所以你会发现,矛盾的点其实就是这个 S3,也就是少数服从多数原则,能保证任意的大多数都是有交集的。交集中的点会发现矛盾和之前接受的值有矛盾选择拒绝。
问题:三节点的容忍度是 1,四节点的容忍度是多少?
答案:也是 1,因为要形成发现矛盾的交集对于 4 来说,要达到 3/4,才能构成大多数,这就是为什么集群选单数的原因,因为双数从算法的角度来说没什么帮助。
接下来看具体的算法。
其实,从朴素角度来说,经典 Paxos 看起来就是一个两阶段提交的过程,首先是准备阶段,选择一个提交号 n,提交 prepare(n),接受者需要返回自己接受的值,和已经接受的提交号。当从大多数收到回复以后就可以做判断了,如果有返回接受值,选择提交号最大的值进行下一阶段(这个行为对应的是发现有值可能被接受了,尝试服从或者学习这个接受),不然就可以用自己的值进行下一阶段。
下一阶段就是 accept(value,n),如果接受者发现自己目前收到的n,没有比accpet给的n大,就接受这个值,并且更新自己的n,否则就拒绝(这里就保证提交者能够发现自己变老了或者被拒绝了)。
如果接受者发现提交号大于自己当前的最大提交号,就接受这个值,不然就拒绝。当提交者从大多数人那里接受到返回以后发现有拒绝的情况,就进行重试拿一个新的n开始,否则这个值就被接受了。
Basic Paxos value 就是设置一次,不存在再设次一次的情况。
总结起来就是如图:
![[basic paxos]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/basic-paxos.png)
那这样的一个二阶段提交,看看能不能解决前面的问题,主要有三种可能。
注意,这里的例子是原文里的例子,一个变量的取值是X或者Y,然后3.1 表示 S1提交的提交号为 3 的提交,这是我们定义的 message ID。
第一种值被选择了,后者意识到了X,放弃 Y 用 X 提交,也就意味着提交者学习到了这个值已经被选择了。
![[situation 1]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/paxos-p1.png)
第二种情况,值没有被选择,但是交集的部分看到了一个被选择的值,也会选择放弃Y用X提交,虽然X暂时没有被选择(被大多数人接受),但是可以保证两个提交都成功。
![[situation 2]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/paxos-conflict-2.png)
第三种情况,值没有被选择,同时交集的部分也没有发现被选择的值,如果已经做了 promies 这个时候就会拒绝老的提交。比如下面在 S3 accept(X) 的时候就会放弃提交并且进行重试(S1 S2 也会一起重试), 并且在重试的时候覆盖掉原先接受的x)。
![[situation 3]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/paxos-conflict3.png)
看起来所有的问题都解决了,但是活性问题无法保证。这个情况发生在提交之间相互阻塞的情况,S3 S4 S5 拿着更高的提交号导致 S1 S2 S3 的 accept 被拒绝重新进行提交,又把 S3 S4 S5 给拒绝了。
![[liveness]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/paxos-liveness.png)
解决这个问题的办法就是把重试时间进行一些随机化,减少这种巧合发生,或者把重试的时间指数增长等等。
Multi-Paxos
到此 classic Paxos 算是告一段落。那 Paxos 有什么问题呢。首先是活性的问题,这个在后面可以通过选主的方式解决。其次是学习是通过 propose 获知值的,不然无法知道一个值是否被接受了,要走一遍整套的 Paxos 协议。
Multi-Paxos 新增的问题是如何选择 log entry,并且用选主的方式减少冲突,以及减少 prepare 的请求。
以下图为例。深色框表示这个 log 已经被选择(怎么确定选择后面会提到)。寻找 log entry 的方式就是寻找第一个没有被选择的 log,尝试执行 basic Paxos,如果有值被选择会尝试用这个 log 提交帮助这个 log 被选择,这个过程和 basic paxos 是一致的,但是在此之后就要继续寻找下一个 log 尝试进行我们的尝试。
下图中(只看 S1 和 S2 这两行),第一次会找到最后一个没有没学习的 log,也就是 index=3 的 log,但是发现了 s1 的 cmp,就会服从这个 cmp,然后到 index=4 发现了 s2 的 sub,也选择服从,并且学习到了 index=4 的 log 应该是 sub,最后到了 index=5 才进行插入。
![[multi-paxos]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/multi-paxos-log.png)
这样的情况下,Paxos 可以接受并发的请求,而 Raft 却规定了对 log 只能 append,不能 3 4 5 都能同时处理,简化了实现。反正只要保证了 log 的顺序一致,状态机的最终状态都是一致的。
接下来的是对于性能的一些提升,一个是选主避免大面积冲突,另一个是优化二阶段提交的次数。解决方法是选出一个主,保证一次只有一个提交者。另外对于 prepare 是对整个 log 进行 prepare,而不是单个 log entry,这样大多数情况下,大部分 log 都可以一次性就被选择。
可以通过 lease based 选主。 lamport 提出的方式比较简单,节点之间维持T间隔的心跳,2T 之内没有收到更高编号的主的心跳就成为主,非主则转发请求给主,这样还是不会避免同时出现两主的情况,两主会有冲突,但 Paxos 就算有两主还是能正常运行,毕竟有主只是优化方式。
接下来我们看看优化提交的过程。回忆一下,prepare 的作用,其中一点是帮助我们发现冲突,知道有值可能被选择了,另外一点是拒绝老的提交,让他们发现自己变“老”了。
我们可以改变提交号的意义,让他代表整个 log,也就是所有 log entry 都用一个提交号,这样接受者可以通过返回 noMoreAccepted 让提交者意识到在当前 log entry 之后的 log 都没有 accpeted 是可以被“锁”住的,然后如果大多数节点返回 noMoreAccepted,就可以跳过之后的 prepare 直到 accept 被拒绝。这样后续的 accept 操作就可以不用 prepare 在一趟之内解决,所以二阶段提交的第一阶段的 promise 落在了整个 log 上。这个情况下 发起者的 accept 一直顺序进行就可以,问题发生在有其他主(之前说到的会临时有多主的情况),又提交了 prepare,然后这个提交号更高,把后一段锁住了,accept 就会发现冲突学习新的值。
补充 1 持续发送 accept 请求,让所有的节点都同步这个 log。
补充 2 让 proposer 带上 firstUnchosenIndex 让 acceptor 知道大多数可以确认被选择的 log。
但是还有问题,例如下面这张图,对于所有小于 firstUnchosenIndex 的 i 来说,如果 accpetedProposal[i] 的提交号和 request 的 proposal 一样的话,就可以确认 log[i] 是被选择了的,并且标记 acceptedProposal[i] = 无限。但是 2.5 确实来自之前的 leader 的,貌似无法被标记为选择了。这需要我们进一步修改这个协议。
![[multi paxos index]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/multi-paxos-index.png)
这个时候需要在 accept 返回的时候带上自己的 firtUnchosenIndex,如果 proposer 的比这个大,可以把 acceptor 直接补齐。用 success 命令,让 acceptor 直接更改index 的这个值, 并且继续返回 firtUnchosenIndex,让 proposer 弥补。
最后一部分是配置改变,degree of replication,也就是要保证同时只有一个 conf 生效,可以用 a 个之前的 log 做 conf,这样在使用这个 conf 之前,conf 已经发生了改变。但是同时限制住了并发度(只能为a)。直觉上讲就是约定一个 index 在某个时间点一次性切换。
![[multi paxos conf]](/zh-CN/2018/05/20/paxos-%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93/multi-paxos-conf.png)
参考文献
![[ca]](/zh-CN/2018/04/30/k8s-%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8E-kubeadm-%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%92%8C%E9%AB%98%E5%8F%AF%E7%94%A8/ca-pic.png)
![[apiserver crt]](/zh-CN/2018/04/30/k8s-%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8E-kubeadm-%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%92%8C%E9%AB%98%E5%8F%AF%E7%94%A8/api-crt.png)
![[boostrap conf]](/zh-CN/2018/04/30/k8s-%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8E-kubeadm-%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%92%8C%E9%AB%98%E5%8F%AF%E7%94%A8/bootstrap-conf.png)
![[kubelet bootstrap conf]](/zh-CN/2018/04/30/k8s-%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8E-kubeadm-%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%92%8C%E9%AB%98%E5%8F%AF%E7%94%A8/kubelet-crt.png)
![[kubelet conf]](/zh-CN/2018/04/30/k8s-%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8E-kubeadm-%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%92%8C%E9%AB%98%E5%8F%AF%E7%94%A8/kubelet-https-crt.png)
![[etcd csr ]](/zh-CN/2018/04/30/k8s-%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8E-kubeadm-%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%92%8C%E9%AB%98%E5%8F%AF%E7%94%A8/etcd-csr.png)
![[symmetric encryption]](/zh-CN/2018/04/26/HTTPS-%E7%9A%84%E5%85%AC%E9%92%A5%E4%BD%93%E7%B3%BB/symmetric-encryption.gif)
![[symmetric encryption]](/zh-CN/2018/04/26/HTTPS-%E7%9A%84%E5%85%AC%E9%92%A5%E4%BD%93%E7%B3%BB/asymmetric-encryption.gif)